Posted on 24/12/2024
Hazardous Plastics Guide
In a world where convenience and durability rule, plastics have become ubiquitous. However, not all plastics are created equal. Certain types of plastics pose significant environmental and health risks, earning the label "hazardous plastics." This guide aims to shed light on these plastics, providing comprehensive knowledge about their hazards, alternatives, and ways to minimize their impact.
Understanding Hazardous Plastics
Hazardous plastics are those that Leach toxic chemicals, persist in the environment, or pose dangers during their lifecycle, from production to disposal. Common types of hazardous plastics include PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), PS (Polystyrene), and certain types of PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate).
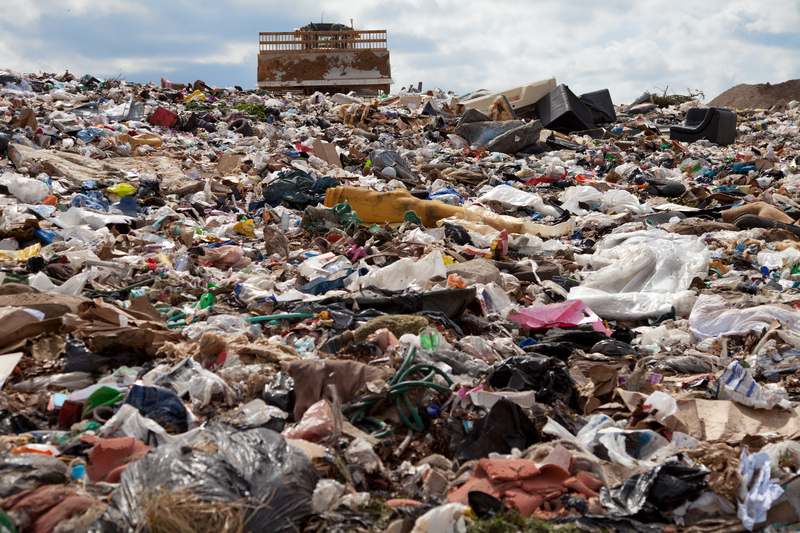

Common Types of Hazardous Plastics
Let's take a closer look at some of the most common hazardous plastics:
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC, often referred to as "vinyl," is widespread in products like pipes, electrical cables, and packaging. The manufacturing and disposal process of PVC releases harmful chemicals like dioxins, which are highly toxic and can cause cancer and other serious health issues.
Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene, commonly known as Styrofoam, is used in food containers, packaging materials, and disposable cups. It contains styrene, a suspected carcinogen that can leach into food and beverages, posing health risks. Additionally, PS is not biodegradable, contributing significantly to plastic pollution.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
While PET is widely recycled, certain types, when exposed to heat, can release antimony trioxide, a toxic chemical linked to respiratory and cardiovascular issues. Single-use PET bottles are particularly troublesome, contributing to litter and landfill problems.
Environmental Impact
Hazardous plastics are notorious for their environmental footprint. They take centuries to decompose, during which they break into microplastics that contaminate soil, water, and the food chain. This persistent pollution affects marine life, wildlife, and human health.
Health Risks
Exposure to hazardous plastics can lead to various health problems, including hormonal disruptions, reproductive issues, and developmental disorders in children. Chemicals like BPA and phthalates, commonly found in hazardous plastics, are known endocrine disruptors.
Safer Alternatives
Fortunately, there are safer alternatives to hazardous plastics:
- Use glass or stainless steel containers for food and beverages.
- Opt for biodegradable or compostable materials.
- Choose plastics labeled as BPA-free or phthalate-free.
- Support companies that use recycled or sustainable packaging.
Tips for Reducing Plastics Exposure
- Avoid using plastic containers in the microwave.
- Reduce the use of plastic wraps and bags.
- Recycle responsibly and support local recycling programs.
- Support legislation aimed at reducing plastic waste.
- Be an informed consumer by reading labels and choosing products with minimal plastic packaging.
Pros and Cons of Plastics
Pros
- Durability and versatility in various applications.
- Lightweight, reducing transportation emissions.
- Cost-effective and easy to produce.
- Recyclable if managed correctly.
Cons
- Environmental pollution and long decomposition time.
- Health risks from chemicals leaching.
- Challenges in recycling and waste management.
- Dependence on fossil fuels for production.

Takeaways
Understanding hazardous plastics and their impact is the first step toward making safer, more environmentally friendly choices. By opting for safer alternatives and reducing plastic use, we can collectively mitigate the harmful effects of hazardous plastics.
Conclusion
Plastics, while highly useful, come with significant drawbacks, particularly when it comes to hazardous types like PVC, PS, and certain PET variants. Awareness and informed choices are crucial in reducing their impact on health and the environment. By adopting safer alternatives and making conscious efforts to minimize plastic use, we can safeguard our planet for future generations.
Latest Posts
Tips for Proper Disposal of Regular Waste
Garbage Cleanup Bags - Efficient Skip Substitute

































 Get a Quote
Get a Quote